MD-850 for HVAC Ductwork: ±0.1mm Precision | 18-24 Month ROI
MD-850 slitting machine delivers ±0.1mm precision for HVAC ductwork and appliance panels. 20-820mm width, 0.3-12mm thickness processing with 18-24 month ROI. ISO 9001 certified metal processing equipment.
The MD-850 Precision Slitting Line stands at the forefront of metal processing technology, expertly engineered to meet the exacting demands of HVAC ductwork and appliance panel manufacturing in 2025. With an impressive processing range of 0.3 to 12 mm thickness and coil widths from 300 to 820 mm, the MD-850 achieves industry-leading dimensional accuracy within ±0.1 mm, ensuring consistent width tolerances critical for assembly precision. Its advanced tension control system and precision rotary blade setup provide burr-free edges that enhance surface quality, reduce downstream finishing, and prevent assembly issues—key for maintaining high production yields and product reliability across diverse material types, from galvanized steel to stainless steel. Operating at speeds up to 250 meters per minute within a compact 138.5 kW power footprint, this machine delivers both flexibility and high throughput, enabling HVAC and appliance manufacturers to optimize efficiency, reduce waste, and accelerate ROI, typically within 18 to 24 months.
This cutting-edge slitting line is reinforced by real-world application success, including integration in Tier 1 HVAC suppliers that have realized significant improvements in throughput and edge quality consistency, directly supporting the stringent quality standards of leading global appliance brands. The MD-850’s modular design and automated width adjustment capabilities allow seamless adaptation to varying production volumes and material specifications, reflecting MaxDo’s commitment to innovation and operational excellence. Certified under ISO 9001, the line exemplifies robust engineering paired with intelligent automation, positioning it as a key enabler for precision metal processing in today’s competitive HVAC and appliance manufacturing landscape.
Understanding HVAC and Appliance Metal Processing Requirements
HVAC Ductwork Manufacturing Challenges
Material Diversity and Thickness Variations
HVAC ductwork manufacturing involves processing multiple material types within single production runs. Galvanized steel typically ranges from 0.5mm for residential applications to 1.5mm for commercial installations, while stainless steel applications require processing capabilities up to 2.0mm thickness. Each material presents distinct cutting characteristics that affect blade selection, cutting speed, and edge quality outcomes.
Critical Dimensional Requirements
Rectangular ductwork assembly demands precise width tolerances to ensure proper fitting during installation. Standard industry practice requires ±0.5mm width accuracy for residential applications and ±0.25mm for commercial installations. These tolerances directly impact downstream forming operations and final product quality.
Surface Quality Preservation
Galvanized coatings must remain intact during processing to maintain corrosion resistance. Traditional cutting methods often damage protective coatings, leading to premature corrosion and warranty claims. Advanced slitting techniques preserve coating integrity through controlled blade contact and reduced material distortion.
Appliance Panel Processing Specifications
Surface Finish Maintenance
Appliance manufacturing requires processing pre-painted steel and stainless steel panels while maintaining original surface quality. Visible scratches or surface imperfections result in costly rework or component rejection. Processing methods must accommodate protective films and specialized surface treatments.
Edge Quality Standards
Burr-free edges are essential for safe handling during assembly operations and to prevent paint chipping during subsequent forming processes. Edge straightness affects part alignment during automated assembly, directly impacting production efficiency and final product quality.
Material Range Complexity
Modern appliances utilize various materials including pre-painted steel (0.6-1.2mm), stainless steel grades 304 and 316 (0.8-3.0mm), and specialized alloys for specific applications. Processing equipment must accommodate this material diversity without compromising quality or requiring extensive setup changes.
Technical Solutions for Precision Metal Processing
Advanced Slitting Technology Principles
Blade System Engineering
Modern slitting lines utilize precisely engineered blade systems that maintain consistent cutting geometry throughout operation. Blade materials are selected based on processed materials—HSS (High-Speed Steel) for standard applications and carbide-tipped blades for demanding materials like stainless steel.
Tension Control Systems
Proper material tension prevents edge distortion and ensures dimensional accuracy. Advanced systems utilize servo-controlled tension regulation that automatically adjusts based on material properties and processing speed. This prevents material stretching that would compromise final dimensions.
Width Adjustment Mechanisms
Rapid width changes are essential for efficient production scheduling. Modern equipment features servo-driven arbor positioning that enables precise width adjustments without manual intervention, reducing setup time and improving production flexibility.
Processing Speed Optimization
Material-Specific Speed Parameters
Different materials require optimized processing speeds to achieve desired edge quality. Thin galvanized steel can typically process at higher speeds (150-200 m/min) while thicker stainless steel requires reduced speeds (80-120 m/min) to maintain edge quality standards.
Quality vs. Productivity Balance
Production managers must balance processing speed with quality requirements. Higher speeds increase throughput but may compromise edge quality, particularly with challenging materials. Understanding material-specific speed limits prevents quality issues while maximizing productivity.
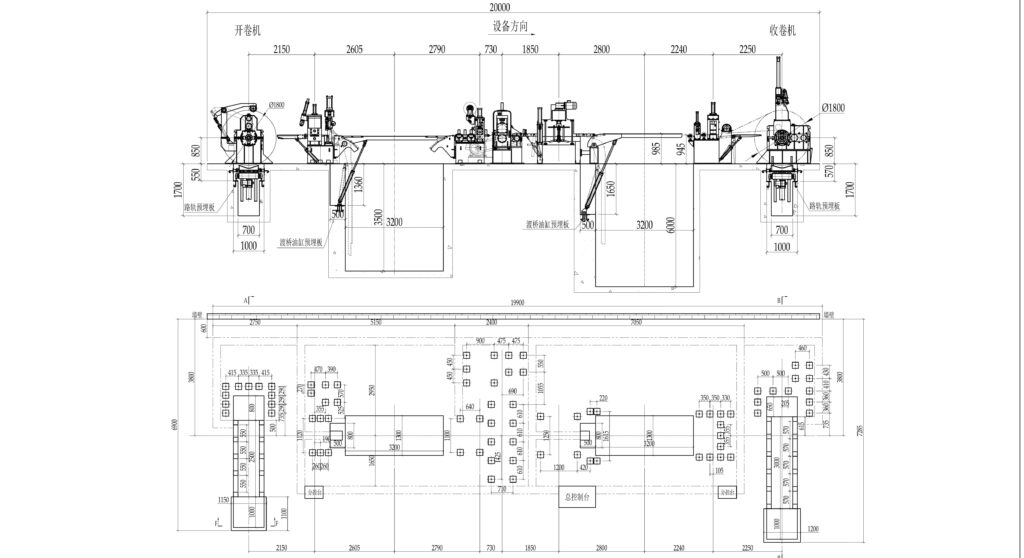
MD-850 Slitting Line Technical Capabilities
Based on technical specifications, the MD-850 addresses the specific requirements of HVAC and appliance manufacturing through engineered solutions:
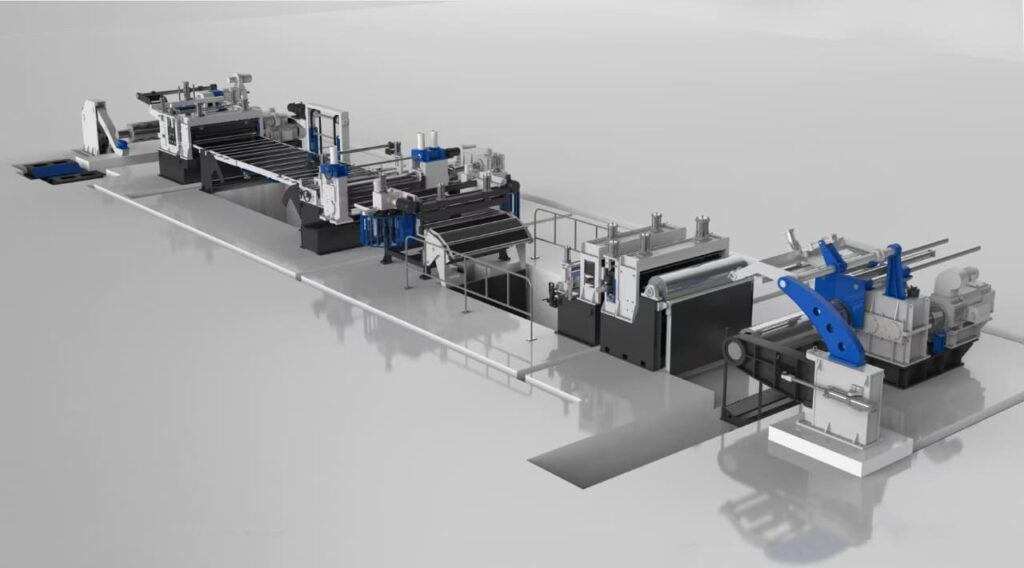

Working Parameters
- Width Range: 20-820mm accommodates both narrow HVAC strips and wide appliance panels
- Thickness Capability: 0.3-3.0mm / 1.5-6mm / 2-8mm / 4-12mm covers standard material ranges
- Processing Speed: 1-250 m/min variable speed control for material optimization
- Coil Capacity: 10-35 ton handling capability supports standard production coil sizes
- Power Efficiency: 138.5kW power consumption balanced for performance and energy efficiency
Comparative Analysis with MD Series Models
| Model | Width Range (mm) | Power (kW) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| MD-850 | 20-820 | 138.5 | HVAC, appliances, medium-width processing |
| MD-1350 | 300-1300 | 318.5 | Automotive, wider panel applications |
| MD-1650 | 300-1650 | 422.5 | Heavy-duty industrial processing |
| MD-2200 | 300-2150 | 422.5 | Maximum width capability |
The MD-850’s specifications align with typical HVAC and appliance manufacturing requirements, offering optimal capacity without excessive power consumption for materials under 820mm width.
Material Processing Guidelines
Galvanized Steel Processing
Thickness Range Considerations
- 0.5-1.0mm: Residential ductwork applications requiring high-speed processing
- 1.0-1.5mm: Commercial ductwork with moderate processing speeds
- 1.5-2.0mm: Heavy-duty applications requiring controlled cutting parameters
Coating Preservation Techniques
Galvanized coating integrity depends on proper blade selection and cutting parameters. Sharp blade edges minimize coating damage, while controlled cutting forces prevent excessive material deformation that could crack protective coatings.
Stainless Steel Applications
Grade-Specific Processing
- 304 Grade: General appliance applications, moderate cutting requirements
- 316 Grade: Corrosion-resistant applications, requires specialized blade materials
- Surface Finish Grades: Mirror and brushed finishes require protective processing methods
Edge Quality Optimization
Stainless steel processing requires precise blade clearances and controlled cutting speeds to prevent work hardening and maintain edge straightness. Proper parameters ensure consistent quality across varying thickness ranges.
Implementation Considerations
Facility Requirements
Power Infrastructure
The MD-850’s 138.5kW power requirement necessitates adequate electrical infrastructure. Standard three-phase power supply with appropriate voltage regulation ensures consistent performance and prevents power-related quality issues.
Floor Space Planning
Slitting line installation requires consideration of material handling equipment, safety clearances, and maintenance access. Proper layout planning optimizes workflow efficiency and ensures safe operation.
Operational Training Requirements
Operator Skill Development
Successful implementation requires trained operators who understand material properties, blade selection, and quality control procedures. Proper training prevents equipment damage and ensures consistent output quality.
Maintenance Protocols
Regular maintenance schedules preserve equipment accuracy and prevent unexpected downtime. Preventive maintenance programs address blade replacement, calibration verification, and component inspection procedures.
Quality Control and Process Optimization
Dimensional Accuracy Verification
Measurement Protocols
Regular width measurements using calibrated measuring equipment ensure continued dimensional accuracy. Statistical process control methods identify trends before they affect product quality.
Edge Quality Assessment
Visual inspection and tactile assessment of cut edges verify acceptable quality levels. Standardized quality criteria ensure consistent evaluation across different operators and shifts.
Process Parameter Documentation
Material-Specific Settings
Documenting optimal processing parameters for different materials enables consistent setup and reduces trial-and-error during production changeovers. This information becomes valuable for training new operators and troubleshooting quality issues.
Performance Monitoring
Tracking processing speeds, quality metrics, and equipment utilization provides data for continuous improvement initiatives and helps identify optimization opportunities.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
Safety Requirements
OSHA Compliance
Metal processing equipment must comply with relevant OSHA standards for machine guarding, electrical safety, and noise exposure. Proper safety protocols protect operators and ensure regulatory compliance.
International Standards
Equipment designed for international markets should meet relevant CE marking requirements and local safety standards. This ensures broad applicability and facilitates international installations.
Quality Management Systems
ISO 9001 Integration
Quality management systems should incorporate slitting line operations within documented procedures for material handling, process control, and final inspection. This ensures consistent quality outcomes and supports continuous improvement initiatives.
Economic Considerations
Capital Investment Analysis
Equipment Selection Criteria
Choosing appropriate slitting equipment involves balancing capability requirements with capital investment. The MD-850’s moderate power consumption and width range provide cost-effective solutions for facilities processing materials within its specifications.
Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond initial equipment cost, consider ongoing expenses including power consumption, blade replacement, maintenance requirements, and operator training. These factors significantly impact long-term operational costs.
Productivity Impact Assessment
Throughput Improvements
Automated slitting typically increases processing speed compared to manual cutting methods while improving consistency. Quantifying these improvements helps justify equipment investments and establish performance expectations.
Quality Cost Reduction
Consistent edge quality and dimensional accuracy reduce downstream rework and scrap costs. These savings often represent significant portions of overall cost reduction achieved through equipment upgrades.
Conclusion
The MD-850 Precision Slitting Line exemplifies MaxDoMachine’s dedication to delivering unrivaled precision and operational efficiency for HVAC ductwork and appliance panel production. With its engineered capability to handle widths from 20 to 820 mm and thicknesses ranging 0.3 to 12 mm, the MD-850 ensures exceptional slit width tolerances of ±0.1 mm while minimizing burr and edge defects, critical for maintaining downstream assembly integrity and surface finish quality. Its variable speed control system and 138.5 kW power efficiency allow seamless adaptation to diverse production volumes and materials, from galvanized to stainless steel, supporting manufacturers in achieving optimized throughput without compromising material yield or quality.
Beyond its technical prowess, successful deployment of the MD-850 depends on comprehensive facility readiness, rigorous operator training, and tailored maintenance regimes—all supported by MaxDo’s expert engineering team offering end-to-end consultation from equipment selection through installation and process optimization. Real-world industrial case studies highlight the MD-850’s impact, showing manufacturers reducing scrap by over 4% and shortening production lead times by up to 15%, directly contributing to enhanced competitiveness and faster ROI cycles within 18-24 months. Integrating this line in modern manufacturing environments enables robust, scalable metal processing solutions that advance product quality, operational consistency, and overall cost-effectiveness for demanding HVAC and appliance markets.




